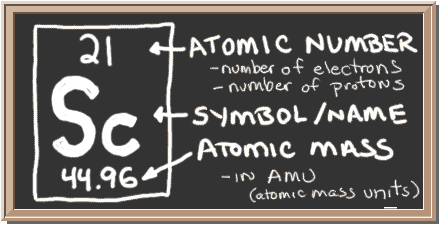
Check out the blackboard. That box on the left has all of the information you need to know about one element. It tells you the mass of one atom, how many pieces are inside, and where it should be placed on the periodic table.
Now we're working with the fourth period/row in the table of elements. You may have an easy way to know the number of electrons in a neutral atom, but the placement of those electrons gets a little more complex. Let's take a look at the arrangements of electrons in the basic elements (left and right sides of the table) of period four and the more complex arrangements of the transition elements (in the middle of the row). If you think this is a little over your head, go back and look at the elements 1-18 that have organizations that are a little more simple.
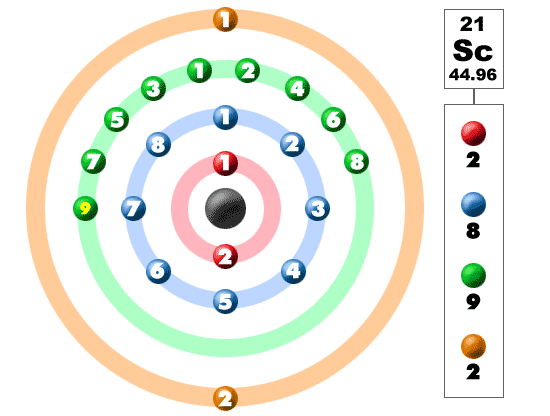
Electrons In The Shells
Take a look at the picture below. Each of those colored balls is an electron. In an atom, the electrons spin around the center, also called the nucleus. The electrons like to be in separate shells/orbitals. As you learn more about atomic structure, you will learn that the electrons don't stay in defined areas around the nucleus. They are found in clouds that can have different shapes that include spheres and dumbbell-like shapes. So remember when you look at our breakdown that the electrons aren't always in a nice neat order as shown here.This element is one of the transition elements that doesn't place the additional electrons in the outer shell, but in the one underneath. For the fourth period/row, all of these electrons build the third shell to a maximum of 18 electrons. Remember that the first eight were placed during our trip through the third period/row. The fourth row of the periodic table has transition metals ranging from scandium (21) to zinc (30).
Ahh, the transition metals. Scandium is the first element of the period table where electron configurations start getting a little wild. Up to this point, you have been using a system of 2-8-8 to describe electron shells. Every element adds one more electron to the outermost shell. Instead of having three electrons in the outer shell, scandium adds its electron to the second to last shell. The electron configuration is 2-8-9-2.
You will find scandium to the right of calcium in the fourth period of the table. Even though its electron configuration is a bit different, scandium still wants to bond with those three extra electrons, no matter what shell they are in.